Bruxism, or the habit of grinding or clenching teeth, is a common issue for many individuals, but for those with autism, it can be particularly challenging. This behavior often goes unnoticed but can lead to serious dental problems and discomfort. It may be linked to stress, anxiety, or sensory sensitivities, and understanding why it happens is the first step in managing it effectively.
Whether it’s during the day or at night, bruxism can impact not just the teeth, but overall well-being. Recognizing the signs and finding ways to help can make a significant difference in improving comfort and quality of life.
Exploring the Connection Between Bruxism and Autism
Research has highlighted a significant association between bruxism, the act of teeth grinding or clenching, and autism spectrum disorder.
Studies have shown that individuals with autism are more likely to exhibit bruxism compared to neurotypical individuals. This correlation raises questions about the underlying factors that contribute to the co-occurrence of these conditions. For individuals with AuDHD (autism and ADHD), the interplay between sensory sensitivities and hyperactivity may further influence the prevalence of bruxism, highlighting the need for tailored interventions.
Several potential reasons may explain the correlation between bruxism and autism. One proposed theory is that bruxism could serve as a sensory or self-regulatory mechanism for individuals with autism. The repetitive nature of bruxism may provide sensory input that helps individuals with autism cope with environmental stimuli or emotional stressors.
Furthermore, communication challenges and difficulties in expressing emotions commonly observed in individuals with autism could manifest as bruxism. The physical act of grinding or clenching the teeth may serve as a form of communication or self-expression for individuals who have limited verbal skills or struggle with emotional regulation.
Understanding these potential reasons for the correlation between bruxism and autism is essential for developing effective intervention strategies and providing support to individuals with autism who experience bruxism.
How to Recognize Bruxism in Autistic Individuals
Understanding and identifying bruxism in individuals with autism is critical for providing appropriate care and management.
Signs and Symptoms of Bruxism
Bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding or clenching, can manifest in various ways in individuals with autism. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of bruxism is essential for early intervention and prevention of potential complications.
Some common indicators of bruxism in autistic individuals may include:
- Teeth grinding or clenching, especially during the day or at night
- Jaw pain or tightness
- Tooth wear or fractures
- Hypersensitivity in the mouth area
- Headaches, particularly upon waking
- Cheek biting or tongue indentations
- Disrupted sleep patterns
Parents and caregivers should be observant of these signs and communicate with healthcare providers if they suspect bruxism in individuals with autism.
That said, diagnosing bruxism in autistic individuals presents unique challenges due to communication difficulties, sensory sensitivities, and behavioral considerations. The complexities associated with autism spectrum disorder can make it challenging to differentiate between voluntary and involuntary movements related to bruxism.
Some common challenges in diagnosing bruxism in autistic individuals include:
- Limited self-reporting capabilities
- Overlapping behaviors with stimming or self-soothing actions
- Difficulty in verbally expressing discomfort or pain
- Sensory issues affecting awareness of oral habits
Healthcare providers and caregivers may need to utilize comprehensive evaluation techniques, including behavioral observations, dental assessments, and collaboration with multidisciplinary teams, to accurately diagnose and address bruxism in individuals with autism.
Early detection and intervention are key in managing bruxism effectively and improving the overall quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Managing Bruxism in Individuals with Autism
Managing bruxism in individuals with autism involves a multidisciplinary approach that takes into account the unique needs and challenges of each individual. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals, including dentists and behavioral therapists, to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
One key aspect of managing bruxism is addressing any underlying causes or contributing factors, such as sensory issues, anxiety, or communication difficulties. By identifying and addressing these triggers, caregivers can help reduce the occurrence of bruxism episodes in individuals with autism.
Additionally, providing alternative sensory outlets, such as chew toys or oral sensory tools, can help redirect the urge to grind or clench teeth. These tools offer a safe and appropriate way for individuals to satisfy their sensory needs without causing harm to their teeth.
Therapeutic interventions also play a vital role in managing bruxism in individuals with autism. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or applied behavior analysis, can help individuals learn alternative coping mechanisms and reduce stress-related behaviors like teeth grinding.
Furthermore, relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, muscle relaxation exercises, and sensory integration therapy, can help individuals with autism manage stress and anxiety, which may contribute to bruxism.
Let’s take a look at some of the most effective therapeutic approaches for managing bruxism in autistic individuals:
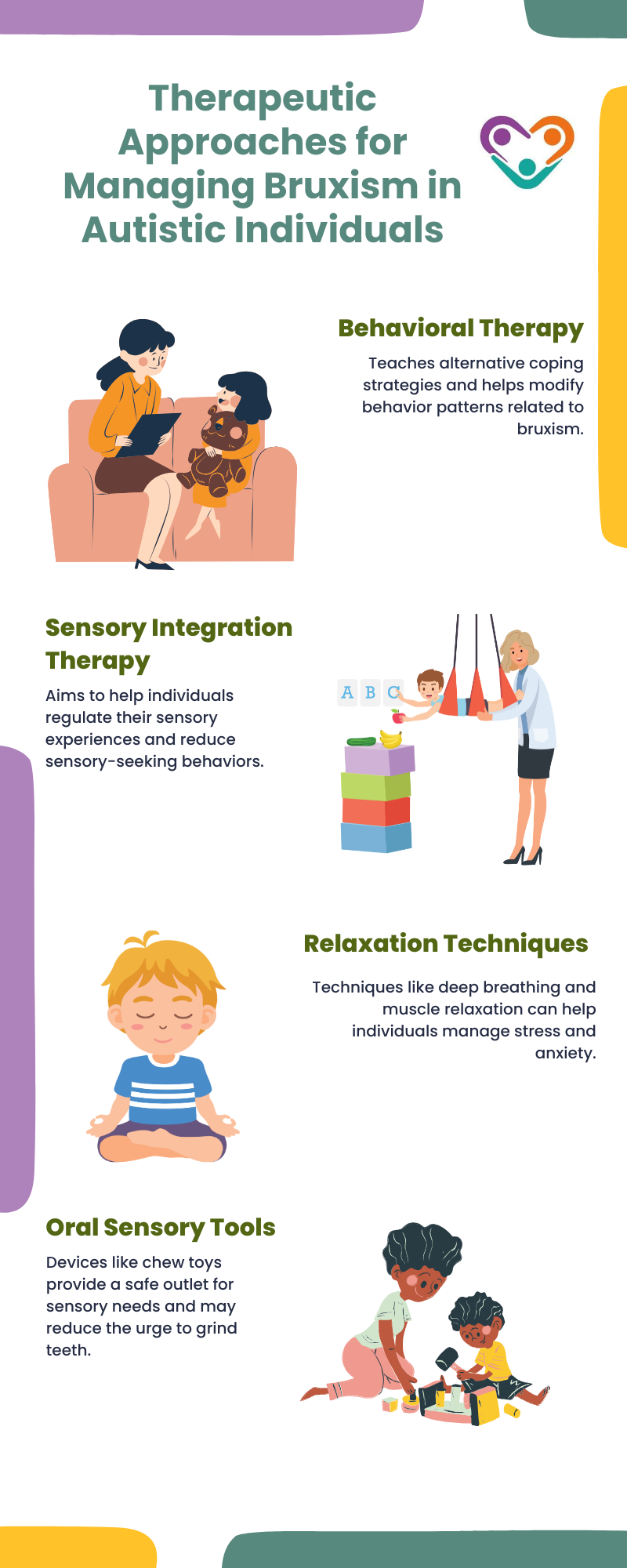
Combining these treatment approaches and working closely with a multidisciplinary team helps caregivers effectively manage bruxism in individuals with autism and improve their overall well-being.
It’s crucial to tailor the treatment plan to the individual’s specific needs and preferences to achieve the best outcomes in addressing this common comorbidity.

Final Thoughts
Bruxism in autism can often be an overlooked concern, but it is important to recognize and address it. Whether it’s grinding teeth during the day or clenching them at night, bruxism can lead to discomfort, damage, and other issues. Identifying the causes – whether they are sensory sensitivities, anxiety, or even medication side effects – can help in finding the right solutions.
Taking proactive measures can make a big difference in managing this behavior and supporting better dental health. At Golden Care Therapy, we offer high-quality ABA services designed to help individuals improve their skills and behaviors in a structured, supportive environment.
Our team is dedicated to working closely with families to develop tailored strategies that foster positive changes. If you’re looking for expert support, don’t hesitate to contact us.
We offer ABA services in Indiana, New Jersey, New York, Georgia, and Florida, and we’re here to help you every step of the way. Reach out today to learn more about how we can assist you and your loved ones in achieving success.
Sources:



