Hand movements in autism can be a fascinating window into how an individual experiences the world. These movements, often referred to as stimming or self-stimulatory behavior, serve various purposes and can provide insight into emotional states or sensory needs.
For many, these actions can be a way to cope with overwhelming feelings, express excitement, or find comfort in routine. Understanding these hand movements is key to appreciating the unique ways that autistic individuals communicate and interact with their surroundings.
Recognizing the significance of these gestures will allow us to foster a deeper connection and support their needs more effectively.
Common Types of Hand Movements
Individuals with autism may exhibit a variety of hand movements, known as stereotypic or repetitive behaviors. These movements serve different functions and can vary from person to person.
Some common types of hand movements observed in autism include:
- Hand Flapping: Repetitive movement of hands, often characterized by rapid opening and closing of fingers.
- Finger Tapping: Tapping or drumming fingers on surfaces or against each other in a rhythmic pattern.
- Hand Rubbing: Rubbing the hands together or against objects in a repetitive manner.
- Clenching Fists: Tightening and holding the fingers in a fist-like position for extended periods.
Understanding the specific hand movements displayed by individuals with autism can provide insights into their sensory processing and communication needs.
The reasons behind hand movements can stem from various factors related to sensory processing, emotional regulation, and communication challenges. These movements may serve as self-soothing mechanisms, ways to cope with overwhelming sensory stimuli, or modes of expressing emotions and needs.
Some common reasons behind hand movements in autism include:
- Sensory Regulation: Hand movements can help individuals with autism regulate their sensory experiences, such as controlling sensory overload or seeking tactile stimulation.
- Expression of Emotions: Hand movements may serve as a non-verbal way for individuals with autism to express their emotions, whether they are excited, anxious, or frustrated.
- Communication: In some cases, hand movements can act as a form of communication, conveying needs, preferences, or discomfort when verbal communication is challenging.
Understanding the underlying motivations behind hand movements in autism is essential for caregivers, educators, and individuals themselves to provide appropriate support and create a nurturing environment that promotes well-being and positive interactions.
Impact of Hand Movements
Hand movements play a significant role in assisting individuals with autism in managing their emotions. These movements can serve as a coping mechanism during times of stress, anxiety, or overwhelm. By engaging in repetitive or self-stimulatory hand movements, individuals with autism may find comfort and a sense of control over their emotions.
It’s been shown that certain hand movements, such as hand flapping or finger tapping, can help regulate emotions by providing sensory feedback and a means of self-soothing.
Understanding and acknowledging the link between hand movements and emotional regulation can aid caregivers and professionals in supporting individuals with autism during challenging moments.
Aside from that, hand movements are also a form of communication and expression for individuals with autism.
Non-verbal gestures, such as hand waving, pointing, or clenching, can convey emotions, needs, or desires when verbal communication is limited. These gestures serve as a bridge for individuals with autism to express themselves and connect with others in their environment.
Recognizing and interpreting hand movements helps caregivers and peers better understand the thoughts and feelings of individuals with autism. Encouraging and accepting these non-verbal forms of communication can enhance social interactions and foster meaningful connections.
How to Address Hand Movements
Understanding and addressing hand movements in individuals with autism is crucial for providing appropriate support and creating a conducive environment for their well-being. Implementing strategies for supporting individuals with hand movements and fostering a supportive environment can significantly impact their quality of life.
In terms of supporting individuals with autism and their hand movements, it’s essential to adopt strategies that are tailored to their specific needs and preferences. Here are some effective strategies for supporting individuals with hand movements:
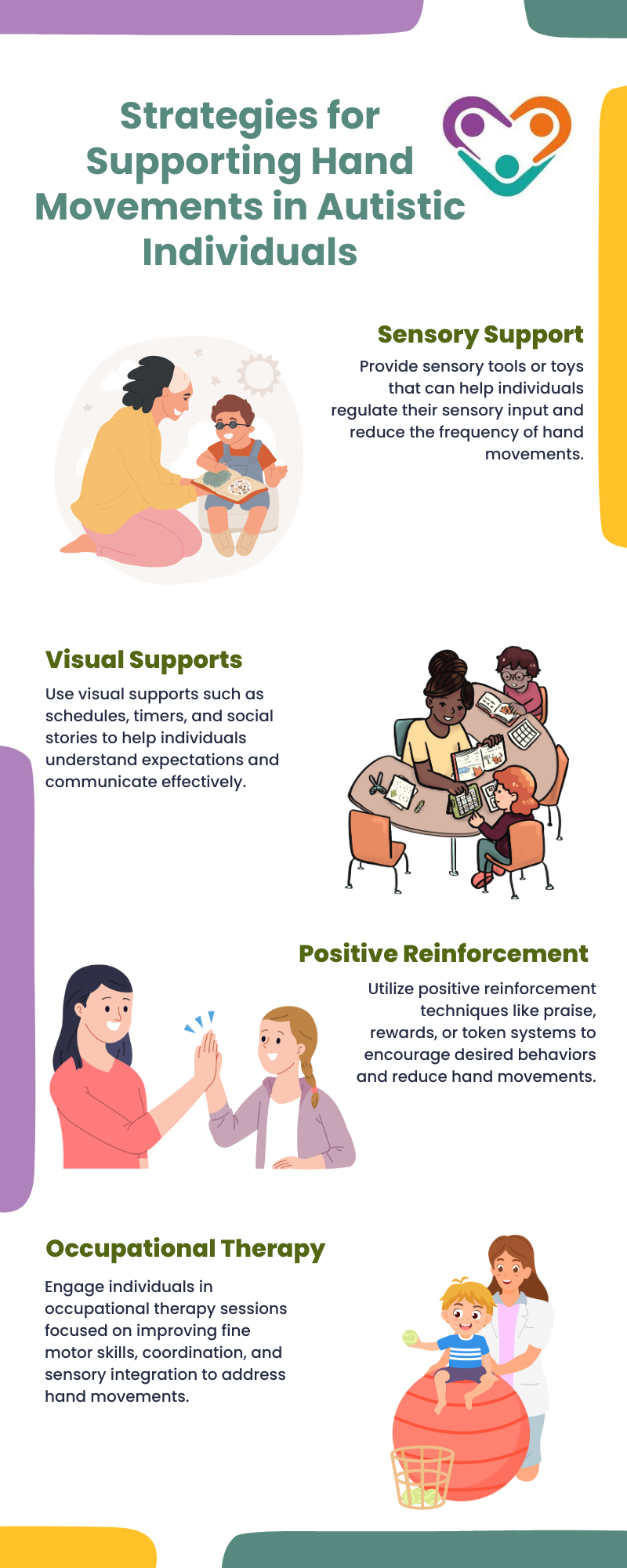
These strategies aim to support individuals with autism in managing their hand movements effectively and promoting their overall well-being.
On the other hand, creating a supportive environment also plays a crucial role in addressing hand movements in individuals with autism. An environment that is understanding, accommodating, and structured can help individuals feel safe, calm, and valued. Here are key elements to consider when creating a supportive environment:
- Sensory-Friendly Space: Design spaces that are sensory-friendly, with minimal distractions, comfortable seating, and appropriate lighting to reduce sensory overload.
- Clear Communication: Use clear and concise language, visual supports, and consistent routines to facilitate communication and understanding for individuals with autism.
- Respect for Individual Differences: Recognize and respect the individual differences and preferences of individuals with autism, ensuring that their unique needs are acknowledged and accommodated.
- Positive and Encouraging Atmosphere: Foster a positive and encouraging atmosphere that promotes self-confidence, autonomy, and a sense of belonging for individuals with autism.
Implementing strategies for supporting hand movements and creating a supportive environment allows caregivers, educators, and individuals themselves to work together to enhance understanding, promote acceptance, and build a nurturing environment for individuals with autism.

The Bottom Line
Hand movements in autism are not just simple gestures; they carry deep meanings and can reveal a lot about how an individual is feeling or interacting with the world. Whether it’s flapping, fidgeting, or other movements, these actions are often a form of self-expression, communication, or sensory regulation.
Understanding these behaviors can help us appreciate the unique ways that individuals with autism connect with their environment.
Embracing and supporting these movements is key to creating a more inclusive world where everyone feels understood and accepted. At Golden Care Therapy, we believe in the power of ABA therapy to foster positive growth and development. Our dedicated team provides high-quality services tailored to meet each individual’s unique needs.
If you’re interested in learning more about our ABA therapy in Georgia, don’t hesitate to contact us today. We’re here to help you navigate this journey and ensure your loved ones receive the compassionate support they deserve.
Sources:

