Social anxiety commonly co-occurs with autism spectrum disorders (ASD), with numerous studies examining the associations between autism and social anxiety symptoms. In order to gain a comprehensive understanding of this co-occurrence, it is important to explore the overview of social anxiety and its associations with autism.
Social anxiety, also known as social phobia, is an intense fear or anxiety related to social situations. Individuals with social anxiety may experience significant distress.
This anxiety can often lead to avoidance of social situations, impacting their daily lives and overall well-being.
In this article, we’re going to explore the connection between autism and social anxiety in adults.
Associations with Autism
Research has shown a significant association between social anxiety and autism spectrum disorders. Studies have found that autistic individuals are more likely to experience social anxiety compared to neurotypical individuals.
Social anxiety in autistic individuals is associated with poorer social skills, functioning, and reduced social motivation. These challenges can further hinder their ability to navigate social interactions and develop fulfilling relationships.
It is important to note that anxiety presents differently in those with autism spectrum disorder compared to neurotypical individuals, as neuroscientists have discovered structural differences in the amygdala of autistic individuals.
The amygdala, which is responsible for emotional memories, plays a significant role in social anxiety disorders in adults with autism.
Impact of Social Anxiety on Autistic Adults
Social anxiety can have a significant impact on autistic individuals, affecting their social skills, functioning, and overall well-being. Understanding these impacts is crucial in providing appropriate support and interventions for individuals with autism and social anxiety.

Social Skills and Functioning
Social anxiety in individuals with autism is often associated with difficulties in social skills and functioning. These individuals may experience challenges in initiating and maintaining conversations, interpreting social cues, and understanding social norms. These difficulties can lead to feelings of isolation, exclusion, and a sense of being misunderstood.
Furthermore, social anxiety may hinder the development of meaningful relationships and limit social participation. Individuals with autism and social anxiety may avoid social interactions or prefer solitary activities to minimize anxiety-provoking situations.
These challenges in social skills and functioning can significantly impact their quality of life and overall social well-being.
Neuroimaging Findings
Neuroimaging studies have provided insights into the brain mechanisms underlying social anxiety in adults with autism.
One area of interest is the amygdala, a structure in the brain that plays a crucial role in processing emotions and emotional memories. Research has shown that abnormalities in the amygdala are associated with social anxiety disorders in individuals with autism.
Specifically, neuroimaging findings suggest that individuals with autism and social anxiety may have an overactive amygdala in response to social stimuli, leading to heightened fear and anxiety responses. This hypersensitivity to social cues may contribute to the development and maintenance of social anxiety symptoms in individuals with autism.
How to Manage Social Anxiety in Autistic Adults
Managing social anxiety in individuals with autism is crucial for their overall well-being and quality of life. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, there are various lifestyle treatments and alternative therapies that can help alleviate anxiety symptoms and improve daily functioning.
Lifestyle Treatments
Lifestyle treatments encompass a range of strategies that aim to create a supportive and nurturing environment for individuals with autism. These treatments focus on modifying daily routines and incorporating activities that promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
One such lifestyle treatment is the implementation of structured schedules and routines. Establishing predictable routines can provide a sense of stability and security, which can help reduce anxiety. Visual aids, such as visual schedules and social stories, can be used to enhance understanding and communication.
Physical exercise is another effective lifestyle treatment for managing social anxiety in autism. Engaging in regular physical activity helps release endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Exercise also provides an opportunity for social interaction, whether it be through team sports or group fitness classes, fostering social skills development.
Additionally, creating a sensory-friendly environment can significantly impact anxiety levels in individuals with autism. This may involve minimizing sensory triggers, such as loud noises or bright lights, and providing calming sensory experiences, such as weighted blankets or fidget toys.

Alternative Therapies
In addition to lifestyle treatments, alternative therapies have shown promise in managing social anxiety in individuals with autism. These therapies aim to address anxiety symptoms through various approaches tailored to the individual’s needs.
Interoception therapy focuses on developing an individual’s ability to recognize and interpret internal sensations and emotions. By improving interoceptive awareness, individuals can better identify and manage their anxiety symptoms.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is another alternative therapy that can be utilized to target anxiety in individuals with autism. ABA techniques help individuals develop skills and behaviors that can reduce anxiety, such as social interactions, coping mechanisms, and emotion regulation.
Alternative Augmentative Communication (AAC) methods, such as using visual supports or assistive technology, can be beneficial for individuals with autism who struggle with communication. AAC provides an alternative means of expressing emotions and needs, reducing the frustration and anxiety associated with communication difficulties.
Sensory diets involve creating personalized sensory activities that meet the individual’s sensory needs. These activities can help regulate sensory input and promote relaxation, reducing anxiety associated with sensory sensitivities.
Expressive art therapy, including activities such as painting, drawing, or music, can serve as a nonverbal outlet for individuals with autism to express their emotions and reduce anxiety. Engaging in creative endeavors can be calming and provide a sense of self-expression.
Medication may also be considered as an alternative therapy for managing anxiety in individuals with autism. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriateness and potential side effects of medication options.
Triggers of Social Anxiety in Autism
For individuals with autism, social anxiety can be triggered by various factors, exacerbating the challenges they face in social situations. Understanding these triggers and their associated symptoms is crucial in developing effective coping strategies.
Social anxiety episodes in individuals with autism can be triggered by factors such as worrying about communication barriers, uncertainties, and stressful situations. The uncertainty surrounding social events or activities can be particularly distressing for autistic adults.
Providing them with advanced information and preparing them for social situations can help alleviate stress and anxiety.
Symptoms of social anxiety in autism can manifest in various ways. Some common symptoms include panic attacks, excessive sweating, self-harm, and an increased risk of weight gain. It is important to recognize that these symptoms may vary among individuals, and each person may have unique triggers and responses to social anxiety.
Coping strategies play a crucial role in helping individuals with autism manage social anxiety. Here are some strategies that can be beneficial:
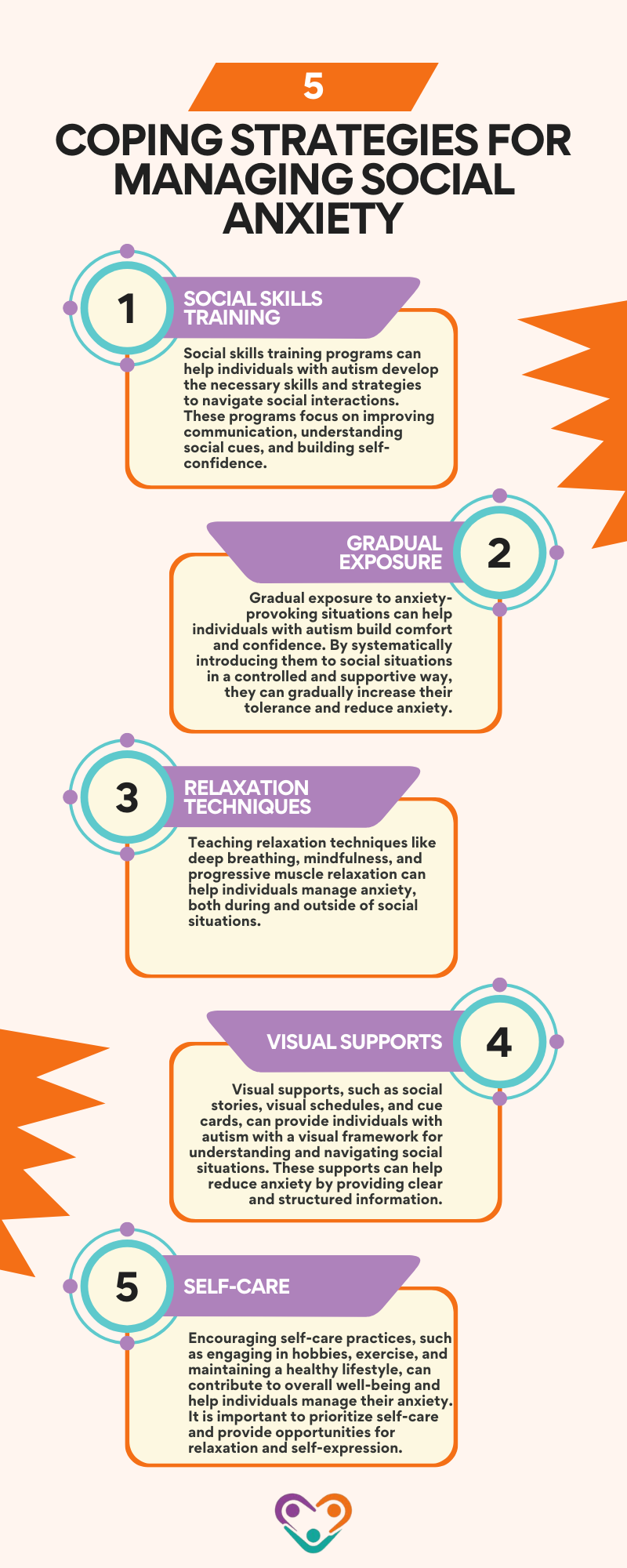
Identifying the factors that trigger social anxiety in autistic individuals and implementing appropriate coping strategies allows us to support them in managing their anxiety and improving their overall well-being.
It is essential to take an individualized approach, considering each person’s unique needs and strengths, to develop effective strategies for coping with social anxiety in the context of autism. For personalized support and guidance, consider reaching out to Golden Care Therapy. We offer specialized ABA services in New Jersey, Georgia, Indiana, and New York. Contact us today to learn how we can help you or your loved one navigate these challenges effectively.

