Visual learning plays a crucial role in the education and overall development of autistic individuals. By understanding visual learners and utilizing visual tools, we can greatly enhance their learning experience and communication skills.
Many children with ASD are visual learners, meaning they process information and learn best through visual stimuli. Visual information is more concrete and lasts longer than spoken or heard information, which helps individuals with autism process information and choose how to respond.
Visual learners benefit from the clarity, permanence, and processing time that visuals offer. Visuals reduce confusion, provide a consistent way to learn and understand the world, and give children extra time to absorb concepts without the pressure of quick verbal responses.

How to Effectively Implement Visual Learning
To effectively implement visual learning strategies for individuals with autism, it is important to consider various techniques and tools that can support their unique needs. It’s worth noting that using visuals could also mean a rise in screen time, and this means that parents and caregivers should learn how to manage screen time for their children accordingly.
Here, we’ll look at three key aspects that are necessary to properly implement visual learning.
Visual Schedules for Organization
Visual schedules play a crucial role in assisting individuals with autism in organizing their daily activities and routines. These schedules provide a visual representation of tasks and events, helping individuals understand the sequence and expectations of their day.
By using visual schedules, individuals with autism can better anticipate and prepare for upcoming activities. This visual support promotes independence, reduces anxiety, and enhances their ability to transition between tasks smoothly.
Teachers, caregivers, and parents can utilize visual schedules to outline the sequence of activities, including school tasks, chores, and leisure activities.
Personalized Visual Supports
Incorporating personalized visual supports is essential when implementing visual learning strategies for individuals with autism. Each individual has unique preferences and needs, and personalized visuals can cater to those specific requirements.
Personalized visual supports can include individualized picture schedules, social stories, and visual cues tailored to the individual’s interests and abilities. These visuals provide clear and concrete information, promoting understanding and engagement.
By using personalized visual supports, teachers and caregivers can adapt lessons and assignments to better serve the needs of individuals with autism. These visuals can help individuals follow instructions, understand expectations, and navigate social interactions more effectively.
Complex Visuals
As individuals with autism progress in their visual learning journey, it is important to gradually introduce more complex visuals. Starting with simple visuals and gradually increasing the level of complexity can help individuals build upon their visual learning skills.
Transitioning to complex visuals may involve utilizing more detailed schedules, incorporating visual aids during conversations, or introducing visual prompts for problem-solving and decision-making. By gradually exposing individuals to more intricate visuals, their visual thinking and processing abilities can further develop.
Flexibility in exploring different visual supports is key during this transition. Some individuals may respond better to visual charts or graphs, while others may benefit from interactive digital platforms.
Being open to different visual tools and adapting to individual preferences can optimize the learning experience for individuals with autism.
Benefits of Visual Tools
Visual tools have a wide range of benefits for individuals with autism. These tools provide a visual representation of information, making it easier for individuals to understand and remember concepts.
Here are some of their key benefits:
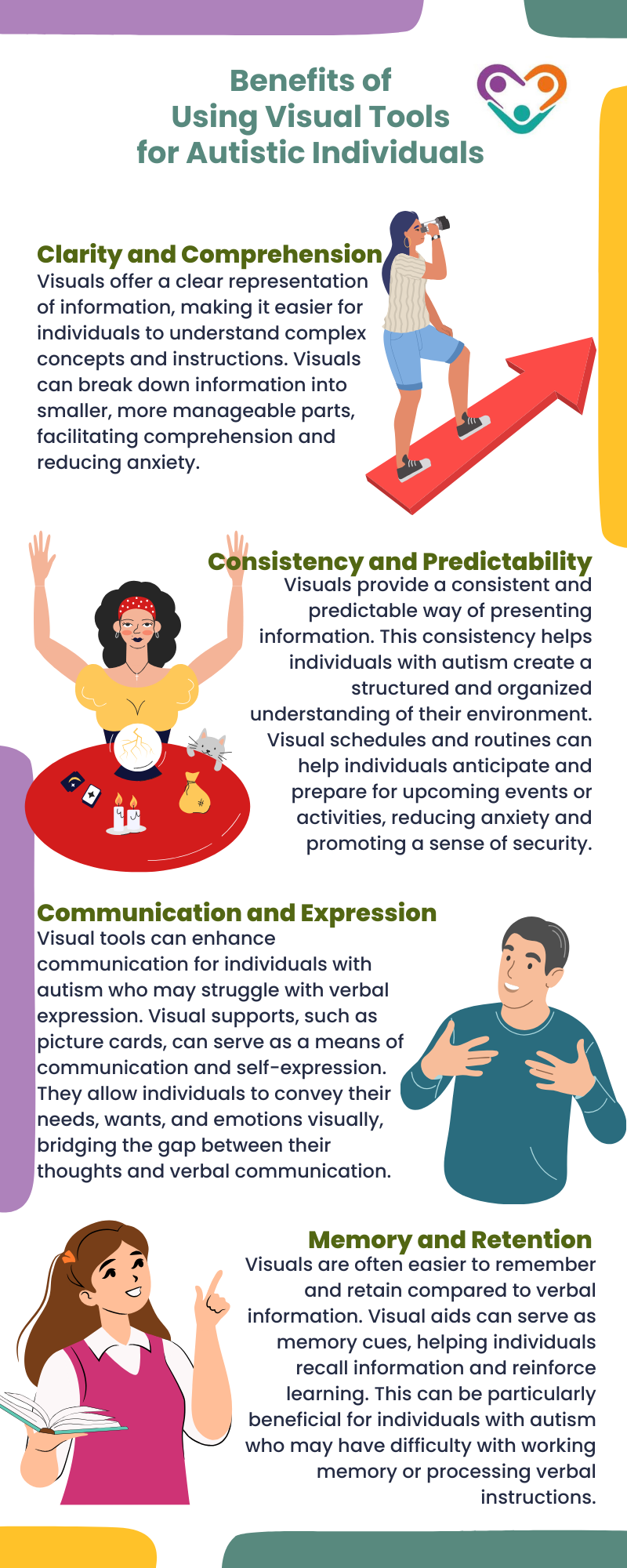
By understanding the unique needs of visual learners with autism and harnessing the power of visual tools, educators, parents, and caregivers can create an environment that supports their learning and communication. Visual learning offers a valuable approach for individuals with autism to navigate the world around them and reach their full potential.
Evolution of Visual Thinking
The concept of visual thinking in autism has gained significant recognition and understanding over the years. One key figure who has played a pivotal role in highlighting the importance of visual thinking is Temple Grandin.
Temple Grandin, who is an accomplished author and speaker, has been instrumental in shaping the understanding of visual thinking in autism. In her book “Thinking in Pictures,” published in 1995, Grandin provided valuable insights into her unique thought process and how she perceives the world through visual images.
Her work has had a profound impact on both professionals and the public, helping to broaden perspectives on autism and learning.
Grandin’s “thinking in pictures” approach has shed light on the strengths and unique abilities of autistic individuals. By sharing her lived experiences, she has helped to foster a greater understanding and appreciation for the visual thinking style that many individuals with autism possess.

Strengths of Visual Thinkers
Autistic individuals often exhibit strengths in visual thinking, which can manifest in various ways. Some of their notable strengths include the following:
- Puzzles and Pattern Recognition – Visual thinkers often excel in solving puzzles and recognizing patterns. Their ability to perceive visual details and make connections can be remarkable.
- Object Organization – Autistic individuals may have a natural inclination towards organizing objects. They often possess a keen eye for detail and can create systems that others may not readily perceive.
- Route Memorization – Visual thinkers tend to have exceptional spatial awareness and can memorize routes with ease. This strength can be particularly useful in tasks that require navigation and spatial understanding.
The strengths of visual thinkers highlight the importance of incorporating visual learning methods in educational and everyday settings. By capitalizing on their inherent abilities, individuals with autism can enhance their learning experiences and maximize their potential.
Visual thinking and learning go hand in hand for many individuals with autism. By utilizing visual tools, such as picture cards, video models, and manipulatives, autistic individuals can better comprehend information, express themselves effectively, and grasp abstract concepts.
These visual aids make learning tasks more accessible and manageable, catering to the unique learning styles of individuals with autism.

Visual Tools for Autism
Visual tools play a crucial role in aiding the understanding, communication, and learning aspects of autistic individuals. These tools help make information more accessible and manageable for autistic individuals which, in turn, enhance their overall learning experience.
There are two commonly used visual tools in this case which are as follows:
Picture Cards
Picture cards are visual representations of objects, activities, or concepts. These cards can be used to support communication, social interactions, and understanding of daily routines. By using picture cards, individuals with autism can better grasp abstract concepts and communicate their needs and preferences.
Picture cards are often organized into visual schedules, which provide a visual representation of the sequence of activities or tasks. This helps individuals with autism understand and follow routines, promoting independence and reducing anxiety.
For example, a visual schedule can include pictures of brushing teeth, getting dressed, and eating breakfast, helping the individual navigate their morning routine.
Video Models
Video models are another valuable visual tool for individuals with autism. Video models provide a visual demonstration of a specific skill or behavior, allowing individuals to observe and learn from the modeled behavior. These videos can be used to teach a wide range of skills, such as social interactions, daily living tasks, and behavior management.
Video models are particularly beneficial for individuals with autism due to their preference for visual learning. By watching video models, individuals can better understand and imitate desired behaviors, improving their social skills and adaptive functioning. For example, a video model can demonstrate how to greet someone, take turns during a conversation, or navigate a social situation.
Visual aids have proven to be highly effective in improving social interactions and time management for individuals with autism. By utilizing tools such as social stories, picture cards, visual schedules, and timers, individuals with autism can thrive in educational and daily life settings.
This results in major improvements in their communication, social skills, and overall well-being.
If you’re seeking specialized ABA therapy in New Jersey, Indiana, Georgia, and New York, Golden Care offers comprehensive services tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual. Contact us to learn more or book a consultation today.
Sources:
https://www.verywellhealth.com/visual-thinking-and-autism-5119992



