Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may be at a slightly higher risk for alcohol problems compared to their peers. This risk becomes even more significant when ASD is accompanied by a diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Due to that, it’s important to understand the risk factors for alcohol problems in individuals with autism and the connection between alcohol use and mental health issues.

Risk Factors for Alcohol Problems
Emerging evidence suggests that many individuals with autism turn to alcohol or drugs as a way to cope with various challenges.
Some of the risk factors for alcohol problems in individuals with autism include:
- Co-occurring mental health conditions – Depression, anxiety, and sleep issues are more prevalent among individuals with ASD compared to the general population. Alcohol use can exacerbate these issues, leading to a potential cycle of self-medication.
- Social difficulties – Individuals with autism often face challenges in social interactions. Alcohol may be used as a means to facilitate social interaction or alleviate social anxiety.
- Sensory issues – Sensory sensitivities are common among individuals with autism. Alcohol may be used as a way to cope with sensory overload or to self-soothe.
- Limited coping mechanisms – Autism can impact an individual’s ability to effectively cope with stress. Alcohol may be seen as a way to escape or numb emotional distress.
While alcohol use has not been shown to directly impact autism symptoms, frequent alcohol consumption can worsen mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and sleep problems. These issues are already more prevalent among individuals with ASD compared to the general population.
It is important to note that alcohol use should not be seen as a solution for these challenges, as it can lead to further complications and hinder overall well-being.

Understanding Alcohol Consumption in Autism
When examining the relationship between autism and alcohol consumption, it is important to consider the unique challenges that individuals with autism face.
Let’s look at what these challenges are.
Social Interaction Challenges
Individuals with autism often experience difficulties in social interactions. These challenges can range from difficulties in understanding social cues and nonverbal communication to struggling with social reciprocity.
As a result, some individuals with autism may feel isolated or have a limited social network.
The impact of these social interaction challenges on alcohol consumption can be complex. Some individuals with autism may turn to alcohol as a means to cope with feelings of frustration, loneliness, or anxiety that can arise from experiencing the world differently than neurotypical individuals.
Alcohol may temporarily alleviate these feelings and provide a sense of relaxation or social lubrication in social situations.
Coping Mechanisms and Triggers
Coping mechanisms play a significant role in the lives of individuals with autism. These individuals may develop unique strategies to manage the challenges they face daily. However, some of these coping mechanisms can be maladaptive, including the use of alcohol.
For some individuals with autism, alcohol may act as a perceived coping mechanism to alleviate stress, anxiety, or sensory overload. The use of alcohol may provide temporary relief from the overwhelming sensory experiences that can be associated with autism.
Triggers for alcohol consumption in individuals with autism can vary. Some individuals may turn to alcohol as a way to navigate social situations or to feel more comfortable in unfamiliar environments.
Others may rely on alcohol as a means to self-medicate for co-occurring mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression, which are more prevalent in individuals with autism.
Understanding the underlying reasons why individuals with autism may consume alcohol is crucial for implementing appropriate interventions and support systems. By recognizing the challenges they face in social interactions and identifying their coping mechanisms and triggers, tailored strategies can be developed to address their unique needs and provide alternative, healthier coping mechanisms.
Prevalence of Alcohol Use in Autism
Understanding the prevalence of alcohol use in individuals with autism is crucial for identifying potential risks and developing appropriate interventions. Let’s look at the rates of substance use disorders in autism and the vulnerability factors associated with this population.
Rates of Substance Use Disorders
Estimates suggest that anywhere from 0.7% to 36% of people with autism may struggle with substance use disorders.
A study proposed a range of 11% to 29% over a person’s lifetime. These figures indicate that individuals with autism are not immune to the challenges of substance abuse and highlight the importance of addressing this issue within the autism community.
Recent research has shed light on the increased vulnerability of autistic individuals to develop substance use disorders compared to neurotypicals. Approximately 11-29% of people with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may experience problems with substance use at some point in their lives.
These findings challenge the traditional belief that individuals on the spectrum have lower rates of alcohol addiction.
It is worth noting that people with ASD tend to have lower rates of substance use compared to other psychiatric disorders. However, individuals with ASD traits, including difficulty expressing needs and adapting to new situations, may still be at risk for alcohol dependence.
In fact, one study found that the more autistic traits a person has, the higher the likelihood of substance use. About 35% of the participants in the study who had six or more autistic traits struggled with alcohol dependence.
Vulnerability Factors
There are several factors that contribute to the increased vulnerability of individuals with autism to substance use disorders. These factors are as follows:
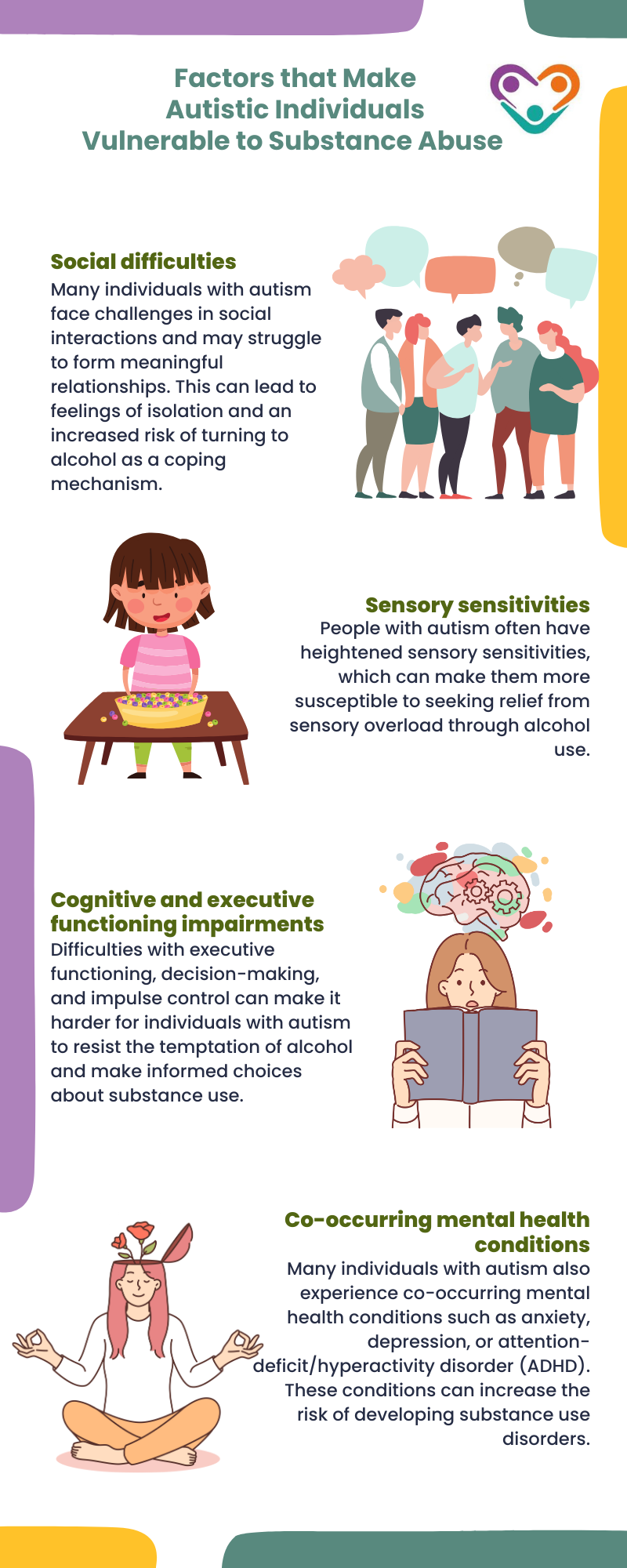
Understanding these vulnerability factors can help inform interventions and support strategies for individuals with autism who may be at risk for alcohol-related issues.
By addressing these factors and providing tailored treatment approaches, it is possible to reduce the prevalence of alcohol use and promote healthier outcomes for individuals with autism.
Interventions and Support for Alcohol Issues
To address alcohol issues in individuals with autism, parents and caregivers can turn to various interventions and support options out there. These can help manage alcohol-related problems and promote healthier behaviors.
Here are the two most effective approaches in this situation:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has shown significant benefits in treating alcohol-related issues in individuals with autism. CBT is a form of therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It aims to help individuals develop healthier coping strategies and improve their overall well-being.
One of the advantages of CBT is its adaptability for use with autistic individuals. Therapists who are knowledgeable about autism can tailor CBT techniques to better suit the unique cognitive profile and needs of individuals on the autism spectrum.
This approach helps address the core anxiety that may underlie the need for alcohol and supports individuals in finding healthier ways to cope with their challenges.
During CBT sessions, therapists work with individuals to identify triggers and underlying emotions that contribute to alcohol use. They help develop personalized strategies to manage cravings, build resilience, and improve social skills. By addressing the underlying issues related to alcohol use, CBT can be highly effective in promoting positive behavior change and reducing alcohol-related problems.
Tailored Treatment Approaches

Tailored treatment approaches specifically designed for individuals with autism are essential in providing effective support for alcohol-related issues. Autism presents unique challenges and needs that require specialized treatment strategies.
These approaches recognize and accommodate the cognitive and sensory differences in autistic individuals, ensuring the interventions are appropriate and effective.
Tailored treatment approaches take into account the individual’s communication style, sensory sensitivities, and social difficulties. By understanding these factors, therapists can create treatment plans that consider the specific needs and preferences of individuals with autism. This approach promotes engagement and improves the likelihood of successful outcomes.
In addition to CBT, other interventions may be incorporated into tailored treatment approaches. These can include social skills training, sensory integration therapy, and stress management techniques. The goal is to provide a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan that addresses both alcohol issues and the unique challenges associated with autism.
In some cases, even regular water intake can be helpful in dealing with alcohol cravings among autistic individuals.
By combining self-awareness with alternative treatment approaches that are specifically tailored to the needs of individuals on the autism spectrum, it is possible to support them in living alcohol-free and addressing the underlying challenges they may face.
Encouraging self-knowledge and providing access to appropriate treatment options can empower individuals with autism to lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their alcohol-related concerns.
Research continues to shed light on the neurological basis of sensory issues in autism, offering hope for more targeted and effective therapies in the future. By recognizing and addressing sensory processing difficulties, we can improve the quality of life for individuals with autism and their families. If you’re seeking specialized ABA therapy in New Jersey, Indiana, Georgia, and New York, Golden Care offers comprehensive services tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual. Contact us to learn more or book a consultation today.
Sources:
https://journeypure.com/ask-our-doctors/alcohol/how-does-alcohol-affect-people-with-autism
https://www.arrowpassage.com/autism-and-alcohol
https://www.autism.org.uk/advice-and-guidance/professional-practice/autism-alcohol
https://www.castlecraig.co.uk/addiction-resources/how-does-alcohol-affect-autistic-people



