Repetitive behaviors are common in autism and can take many forms. These behaviors might seem unusual to those who are not familiar with autism, but they serve important functions for those who experience them.
Whether it’s repeating certain actions, making specific sounds, or focusing intensely on particular objects or topics, these behaviors provide comfort, help manage anxiety, and offer a way to interact with the world.
Understanding these repetitive behaviors can help support individuals with autism and appreciate the unique ways they navigate their surroundings.
Types of Repetitive Behaviors
Repetitive behaviors can surface in diverse ways, and they reflect the unique characteristics of each individual. These behaviors, classified by researchers, are delineated into two main categories:
- “Lower-Order” Behaviors: These include behaviors like fidgeting, hand-flapping, and repeating words or phrases.
- “Higher-Order” Behaviors: These include a preference for sameness, routine adherence, and intense interests.
These categorizations help to differentiate between outward physical actions and more intrinsic behavioral patterns that individuals with autism may exhibit.
Repetitive behaviors in autism can manifest in a spectrum of actions, spanning from mild to severe, with varying impacts. While these behaviors may not be limited to individuals with autism, they can significantly affect social interactions and daily functioning if they become overly pronounced.
Common examples of repetitive behaviors in autism include:
- Arm or hand-flapping
- Finger-flicking
- Rocking
- Jumping
- Spinning
- Head-banging
- Complex body movements known as ‘stimming’ or self-stimulating behaviors
These behaviors often serve as coping mechanisms or self-regulatory actions, aiding individuals in managing sensory overload or stress. It’s crucial for caregivers and support systems to identify these behaviors and provide appropriate strategies to help individuals with autism navigate their daily lives more effectively.
Understanding the diversity of repetitive behaviors in autism is key to promoting awareness, acceptance, and informed support within the community. By recognizing the nuances of these behaviors and their impacts, caregivers and individuals alike can work towards creating inclusive and accommodating environments that cater to the unique needs of those with autism.
Categorizing Repetitive Behaviors
To understand repetitive behaviors in individuals with autism, researchers have categorized these behaviors into two distinct groups: “lower-order” behaviors and “higher-order” behaviors.
Lower-order behaviors typically encompass more observable and physically engaging actions. These can include repetitive movements such as finger-flicking, hand-flapping, rocking, spinning, jumping, twirling, and other complex body movements.
These behaviors are often referred to as ‘stimming‘ or self-stimulating behavior and can serve as a way for individuals with autism to regulate their sensory experiences or express their emotions.
On the other hand, higher-order behaviors involve more cognitive patterns and preferences. This category may include a strong preference for sameness and routine, resistance to change, and intense interest in specific topics or activities. Individuals exhibiting higher-order repetitive behaviors may feel a heightened sense of comfort and security in familiar environments and routines, finding reassurance in predictability.
Understanding the distinction between lower-order and higher-order behaviors is crucial in developing effective strategies for supporting individuals with autism in managing their repetitive behaviors.
Manifestations of Repetitive Behaviors
Autistic perseveration, which is a form of repetitive behavior, may not be readily apparent to observers unfamiliar with autism. This behavior is characterized by a person repeatedly engaging in the same actions or speech patterns.
One common example is reciting a memorized speech on a particular topic in an identical manner, including using the same words, tone, and gestures.
Autistic individuals may find comfort and security in these repetitive behaviors, and they can serve as coping mechanisms in stressful situations.
Understanding these manifestations can help caregivers and individuals navigate these behaviors with patience and empathy, fostering a supportive environment for those with autism.
Some autistic individuals may exhibit violent stereotyped behaviors that pose challenges to both the individual and their caregivers. These behaviors can include head-banging, aggressive actions towards oneself or others, or engaging in repetitive physical actions like rocking, flicking, or pacing. It’s crucial to address these behaviors with understanding and appropriate intervention strategies to ensure the safety and well-being of the individual.
When managing violent stereotyped behaviors, it’s important to focus on identifying triggers and implementing preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of these behaviors occurring.
Interventions such as creating a calming environment, providing sensory tools, and teaching coping mechanisms can help individuals manage their emotions and alleviate the need for harmful repetitive actions.
Challenges and Management
For individuals with autism, routines play a crucial role in providing structure, predictability, and a sense of security. However, managing these routines can be particularly challenging when disruptions occur, leading to stress and anxiety.
Hence, caregivers should understand the impact of routine disruptions on individuals with autism and implement strategies to help them cope effectively.
To cope with routine disruptions, it’s essential to establish clear communication, prepare the individual in advance for any changes, provide visual schedules or cues to aid in understanding transitions, and offer support and reassurance during challenging situations.
Managing repetitive behaviors in autism requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the function of the behavior, sensory sensitivities, and individual preferences. Here are some effective strategies for managing repetitive behaviors include:
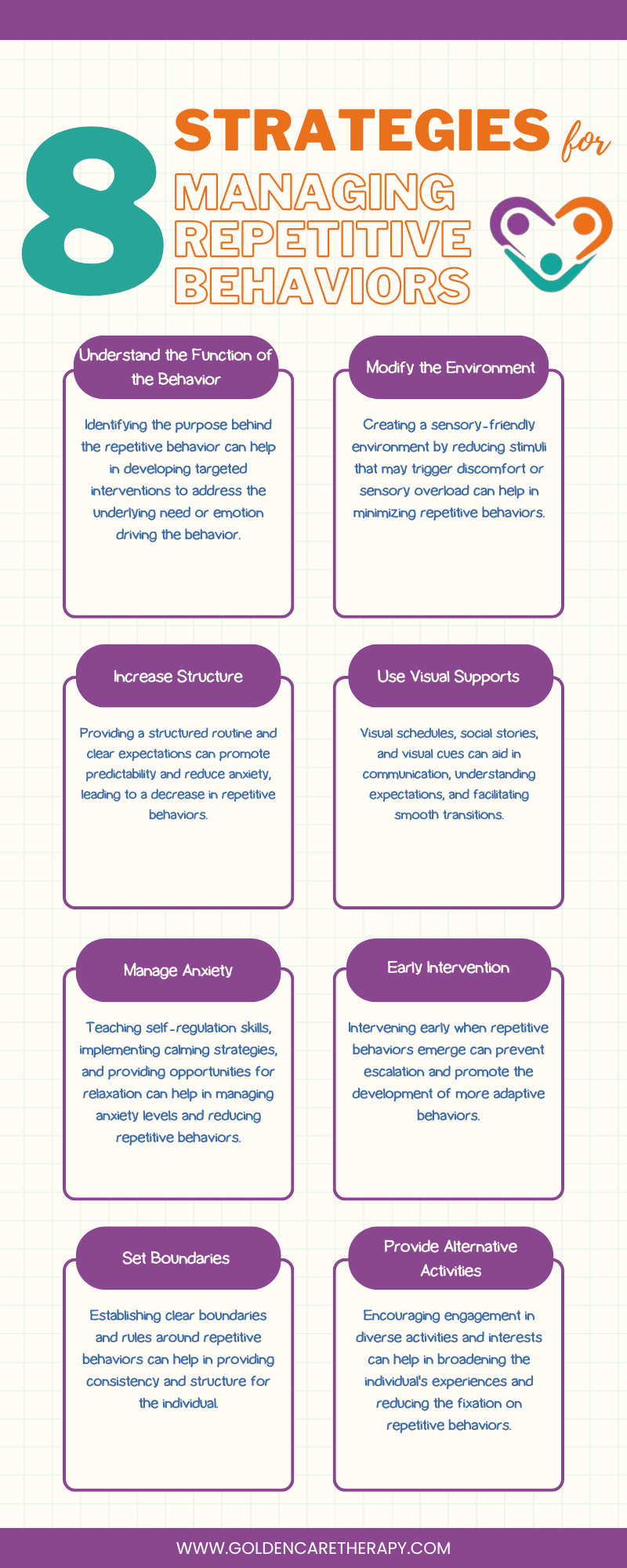
Implementing these strategies and approaches will allow caregivers and individuals with autism to work together to effectively manage repetitive behaviors, enhance daily functioning, and improve overall quality of life.
Making small, achievable goals, providing support, and fostering a balanced approach towards engaging in interests and other activities are key to promoting positive behavior outcomes. For tailored support and guidance, consider exploring ABA services in New Jersey, Georgia, Indiana, and New York from Golden Care Therapy. To learn more about how we can assist you, please contact us for more information and personalized help.
